|
HOME
TRENDS
BACKGROUND
TERMS
ABOUT
|
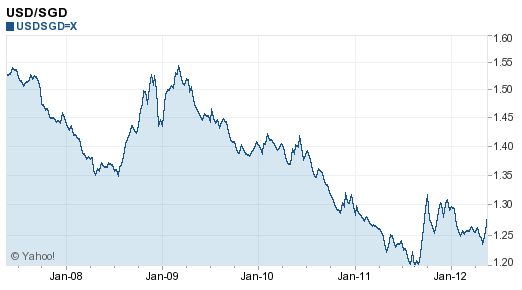
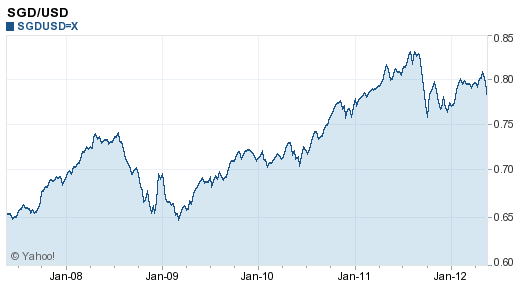
1 USD = 1.4830 SGD 1 SGD = 0.67431 USD
All over the headlines is news about the Global Financial Crisis currently being experienced by economic markets all over the world, which began with the credit crunch in late 2007, causing a loss of confidence in US investors, who backed out from their investments. This in turn caused the US federal bank to pump in large investment capital into financial markets, giving rise to the plummeting consumer confidence as stock markets all around the world crashed.
The collapse of the Lehman Brothers just a month ago on September 14, 2008 marked a new phase of the crisis, where many financial institutions faced strings of serious liquidity issues, and Singapore was not spared.
As such, investors have lost confidence in financial markets, pulling out of their investments and taking the safe route lest the worst - the crashing of the market - happens.
Relative to the USD, the SGD has appreciated, though there is still an overall drop in the exchange rates on both sides.
If you intend to travel to the USA...
Airline ticket prices are expected to plunge further as less people prefer to travel during difficult times of recession. In the meantime, we would suggest that you wait should you wish to exchange the SGD for USD, as the SGD value is expected to appreciate further relative to the USD.
|
WELCOME! :)
This is a blog that houses what two economists have to say about economic exchange rates between Singapore (where we're based at!) and the global economic powerhouse, the United States of America.
So if you're looking for opinions, advice or even predictions, you're at the right place! ENJOY ;)
Currently:
Significant economic events:
only those affecting SGD/USD will be stated
[2008] Global Financial Crisis
[2009] Global Financial Crisis
[2011] U.S. Debt Crisis
[2012] U.S. Debt Crisis
|
economic terms
appreciation
An appreciation means an increase in the value of a currency, such that it is worth more in terms of foreign currency.
For example, when SGD1 = USD1, an appreciation of the Singapore Dollar would likely be SGD1 = USD1.5. As such, more USD can be exchanged with the same amount of SGD, showing that the value of SGD has increased relative to USD.
depreciation / devaluation
A depreciation/devaluation of a currency implies a decrease in its value, such that it is worth less in terms of foreign currency.
circular income-flow
This is the basis for Keynes’ income-expenditure model, explained later below, that came to play a big part in the study of economics. It is taken to be that as long as there are available resources, firms will keep producing while consumers will continue to spend on these products. As long as this continues, the economy is said to be in equilibrium. However, there are two other important types of flow of income: 1) Injections, and 2) Leakages. Injections keep the income in the circular flow while leakages withdraw this income, or purchasing power, from the system.
keynes’ income-expenditure model
JM Keynes is a legendary British economist, who is largely remembered for his theory on the circular flow of money in an economy, still widely in use today. He provided many insights into the workings of the macroeconomy, such as injections and withdrawals, the multiplier, the role of expectations in influencing consumption and investment decisions as well as the role of the government in initiating fiscal pump-priming.
Keynesian analysis of the income-expenditure model is built around the central concept of Aggregate Expenditure (AE). National income is equal to aggregate expenditure, which is comprised of consumption, investment, government expenditure, and net export (taking away import).
NY = AE = C + I + G + X - M.
This also led to many other economic terms commonly used today, such as his famous "animal spirits".
Consumer Price Index
This records the changes in the price level of consumer goods and services purchased by households, recorded in index numbers. It is a useful tool in determining whether exchange rates are weak or strong in relation to each other.
Purchasing Power Parity
Currencies differ in economies all over the world. Currencies can also buy different things in each economy. Purchasing Power Parity or PPP shows how much the same amount of money (in different currencies) can buy.
background information
Exchange rate policies are policies adopted by the government with regards to the exchange rate between currency of the country with currency of other countries. It
• affects a country’s monetary policy
• differs from country to country
A currency is managed against basket of currencies of major trading partners and competitors. Various countries given varying degrees of importance / weight, depending on trade dependence with the particular country.
For Singapore, monetary policy has been centred on the management of the exchange rate. The primary objective is to “promote price stability as a sound basis for sustainable economic growth” and therefore the exchange rate policy adopted by the Singapore government also aims to do so.
* Choice of exchange rate as immediate target of monetary policy means MAS gives up control over domestic interest rates & money supply.